Foreign Reserves Management Report - 2023
The Political Constitution of Colombia and Article 14 of Law 31 of 1992 assign Banco de la República (the Central Bank of Colombia) the function of managing Colombia's foreign reserves. Las opiniones y posibles errores son responsabilidad exclusiva del autor y sus contenidos no comprometen al Banco de la República ni a su Junta Directiva.
Foreign reserves are managed by Banco de la República (the Central Bank of Colombia) as per the rules established by the Political Constitution of Colombia and Law 31 of 1992 and in accordance with the criteria of safety, liquidity, and return. Banco de la República maintains foreign reserves in the amounts it considers sufficient to maintain adequate external liquidity for the country. The level of foreign reserves is a determining factor in the perception of the payment capacity by domestic borrowers.
Main characteristics of Banco de la República's reserves management policy
- Reserves are invested in financial assets with high levels of safety and liquidity, characterized by a large secondary market.
- The percentage of reserves that remains available to cover immediate liquidity needs, called working capital (i.e., invested in the very short term), remains at low levels. This is because under a floating exchange-rate regime, the probability and amount of potential intervention in the foreign exchange market by the central bank is low.
- Considering the lower liquidity needs in the current exchange-rate regime, the rest of the investment portfolio has a longer term and higher expected return, which maintains a low risk level.
- Reserve management policies are based on modern portfolio theory, which suggests applying the principle of diversification, since it is impossible to predict with certainty the behavior of each of the investments in a portfolio. In this way, the safety, liquidity, and return of the portfolio are evaluated as a whole and not by the performance of individual investments.
- The administration of foreign reserve resources is carried out through portfolios managed directly by Banco de la República and those managed by specialized external firms.
Current situation of Colombia’s foreign reserves
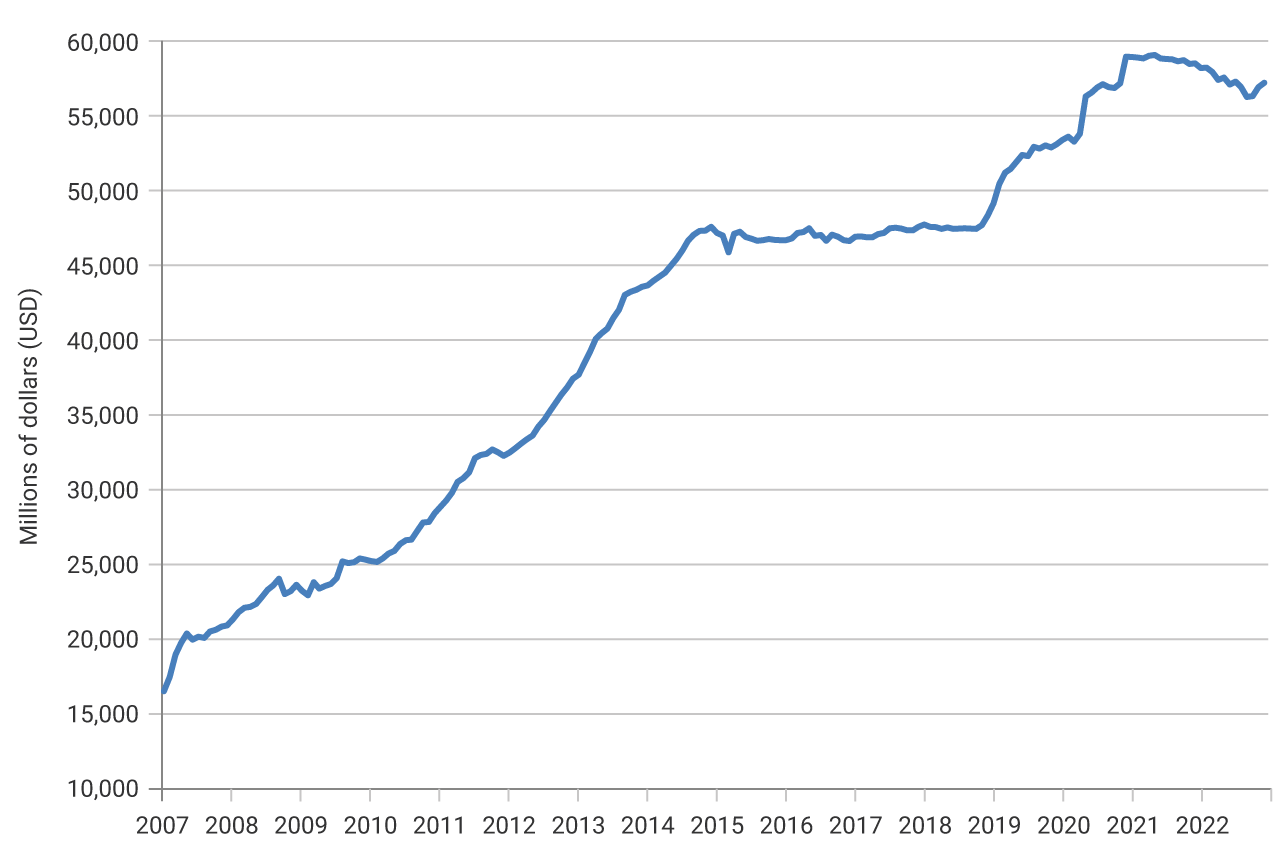
Net foreign reserves totaled USD 57,269.2 m on 31 December 2022.
Graph 1. Colombia’s Net Foreign Reserves
- Different indicators to assess the level of foreign reserves indicate adequate levels for the country.
- An indicator widely used internationally to measure the adequate level of foreign reserves is the Assessing Reserve Adequacy (ARA) methodology. This metric is proposed by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and establishes that reserves should cover the main balance of payments risks in periods of pressure in the foreign exchange market. An economy is considered to maintain adequate levels of reserves if the reserve adequacy indicator is between 1.0 and 1.5. With figures as of December 2022, the IMF’s reserve adequacy indicator calculated for Colombia was 1.32.
Composition of the foreign reserves
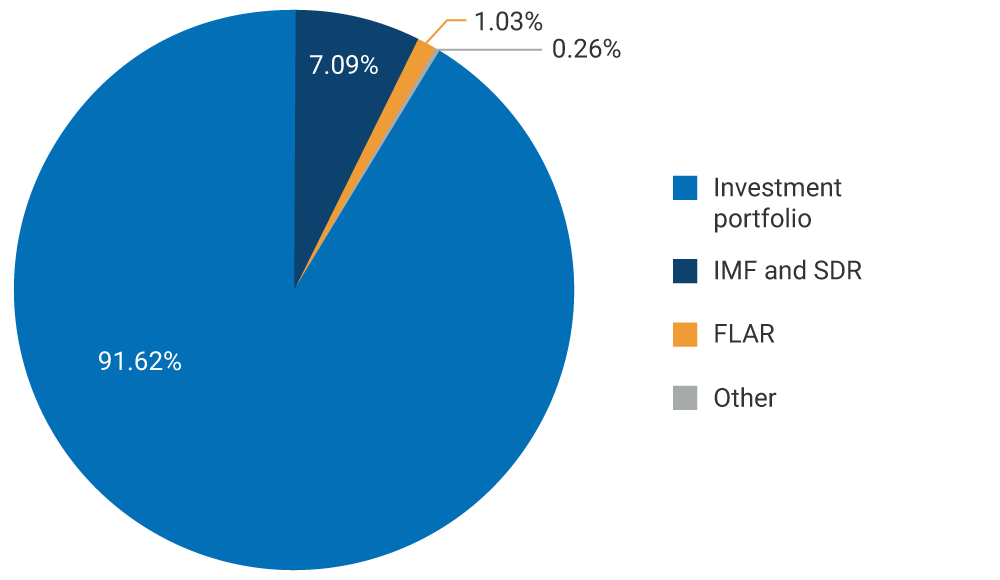
The main component of foreign reserves is the investment portfolio with 91.62% of the total (USD 52,488.71 m). The remaining balance is distributed among the position in the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and Special Drawing Rights (SDR), contributions to the Latin American Reserve Fund (FLAR in Spanish), and others.
Graph 2. Composition of Foreign Reserves
The investment portfolio is composed of a short-term and a medium-term tranche.
- The short-term tranche is intended to cover the potential liquidity needs of the reserves in twelve months.
- The medium-term tranche seeks to increase the expected return on foreign reserves in the long term, preserving a conservative portfolio with an expected return profile higher than that of the short-term tranche.
Composition of the investment portfolio by sector
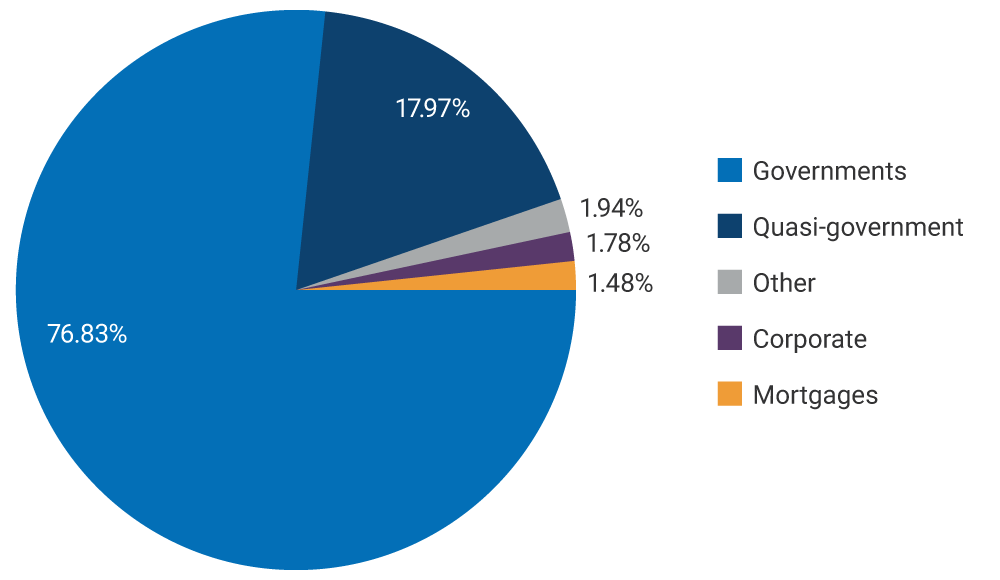
At the end of December 2022, foreign reserves consisted primarily of securities issued by governments and government-related entities.
Graph 3. Composition of the Investment Portfolio by Sector
Foreign exchange composition of the investment portfolio
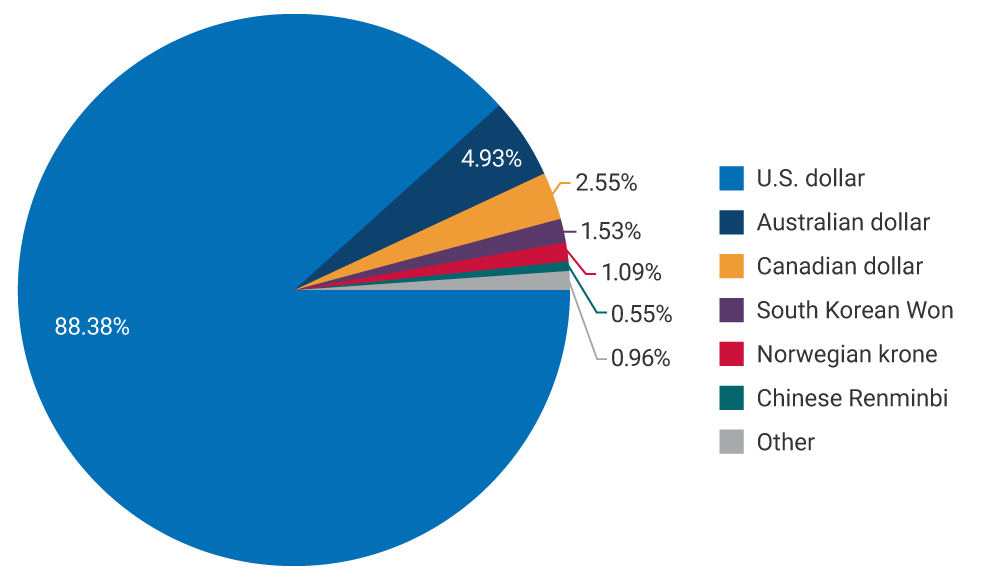
Foreign reserves are comprised of currencies that are characterized by high daily trading volumes and belong to countries with high credit ratings, with the U.S. dollar being the currency with the largest share.
Graph 4. Foreign Exchange Composition of the Investment Portfolio
Composition of the investment portfolio by credit rating
The composition of the portfolio by credit rating evidences the high credit quality of the assets in which the portfolio is invested. As of 31 December 2022, 82.49% of the portfolio was invested in AAA rated instruments.
Managing the risks associated with the investment of reserves
The security criterion with which foreign reserves are managed in Colombia implies adequate control of the risk to which investments are exposed. Some of the main risk management policies are as follows:
- To manage liquidity risk, the Bank defines investment tranches based on the portfolio’s liquidity and return objectives and invests in financial assets that are easy to liquidate in the secondary market.
- Banco de la República seeks to limit market risk by investing in a limited group of eligible assets with moderate sensitivity to interest rate movements.
- The Bank defines minimum credit ratings and maximum concentration limits per issuer to prevent credit events and mitigate their impact. Currently, the minimum long-term credit rating for debt securities eligible for the reserve portfolio is A-.
- In order to invest reserves with high safety and liquidity, investments in the following currencies were permitted at the end of 2022: US dollar, Canadian dollar, Australian dollar, New Zealand dollar, Hong Kong dollar, Singapore dollar, Swedish krona, British pound, Swiss franc, euro, yen, Norwegian krone, renminbi, and Korean won. All of these currencies are characterized by large public debt markets, highly traded foreign currencies, and governments with credit ratings that comply with investment guidelines of Banco de la República.
- To mitigate counterparty risk, payment-on-delivery mechanisms are used, requirements and exposure limits are established for the counterparties with which the portfolio transactions are carried out, and framework agreements are signed with such counterparties.






























































