Strategic Plan 2026-2029
Governor’s Letter
I am pleased to present the Strategic Plan 2026-2029, approved by the Board of Directors of Banco de la República (the Central Bank of Colombia) in November 2025, which outlines the themes and objectives that will guide our management over the coming years. The strategic objectives are framed within the mission to:
“Contribute to the well-being of Colombians by preserving the purchasing power of the currency, supporting sustainable growth in economic activity and employment in coordination with general economic policy, contributing to financial stability, the proper functioning of payment systems, the generation and dissemination of knowledge, and the country’s cultural activity.”
To prepare the Plan, working sessions were held in which we worked jointly with the Board Members, the Deputy Technical Governor, and the Deputy Executive Governor, as well as the Chief Officers who, together with their teams, gathered and articulated the initiatives of their areas over several months. This exercise assessed economic, technological, social, and environmental trends within the framework of central banking, as well as their potential impact on the Bank’s functions.
The Strategic Plan 2026–2029 will be subject to close monitoring throughout its development.
I invite you to review its contents:
- I. Introduction
- II. Banco de la República’s Mission, Vision, Values, Functions, and Services
- III. Strategic Themes
- IV. Monitoring of the Strategic Plan

I. Introduction
The Strategic Plan 2026-2029 (hereinafter, the SP 26-29) sets out the themes and objectives that will guide the management of Banco de la República (the Bank) over the medium term. Through this new strategic planning cycle, the Bank seeks to consolidate the progress achieved in previous years; guide and prioritize its actions based on the trends that will impact central banking; and contribute to the fulfillment of its main objective of preserving the purchasing power of the currency, in coordination with the general economic policy1.
Article 2 of Decree 1739 of 25 October 2017, which amended the Bank’s Bylaws, established the obligation of its Board of Directors (BDBR) to approve a strategic plan and a medium-term expenditure framework under the following terms:
“The Board of Directors shall annually approve a medium-term expenditure framework (for its operation and for investment) effective for the following 5 years. Likewise, every 4 years, it shall approve a strategic plan for the following 4 years, which shall be reviewed annually.
Approval of the annual budget, the medium-term expenditure framework (for operation and for investment), and the strategic plan shall require the affirmative vote of 5 members of the Board of Directors.”
For the formulation of the SP 26-29, the Bank’s senior management analyzed global trends impacting central banking, corporate management, and cultural activity. This exercise was complemented by a review of the current strategic plan, the Bank’s institutional specificities, and a comparative assessment of the strategic plans of a representative sample of benchmark central banks.
To prepare the SP 26-29, working sessions were held with the participation of the Bank’s Board Members, the Governor, the Deputy Technical Governor, and the Deputy Executive Governor, as well as the Chief Officers. Following these sessions, eight strategic themes were defined, each structured around a set of medium-term institutional objectives2. These objectives are aimed at further contributing to the well-being of Colombians and strengthening the institutional capacity to address future challenges.
This document is divided into four sections, including this introduction. The second section presents the Bank’s mission, vision, values, and its functions and services. The third section describes the strategic themes and objectives, and the fourth section presents the monitoring framework for this SP 26-29.
II. Mission, Vision, Values, Functions, and Services of Banco de la República
As part of the development of the new Strategic Plan, the Governor and the members of the Board reviewed the Bank’s mission, vision, and values, which are presented below, together with its functions and services:
A. Misión, visión y valores
B. Functions and Services
The Bank’s functions and services are grouped into two categories: missionary and related functions. Both fall within the authorizations and mandates granted by Law 31 of 1992. Missionary functions correspond to the essential activities of central banking, while related functions correspond to those that support these functions or are related to cultural management (Graph 1).
Graph 1. Functions and Services
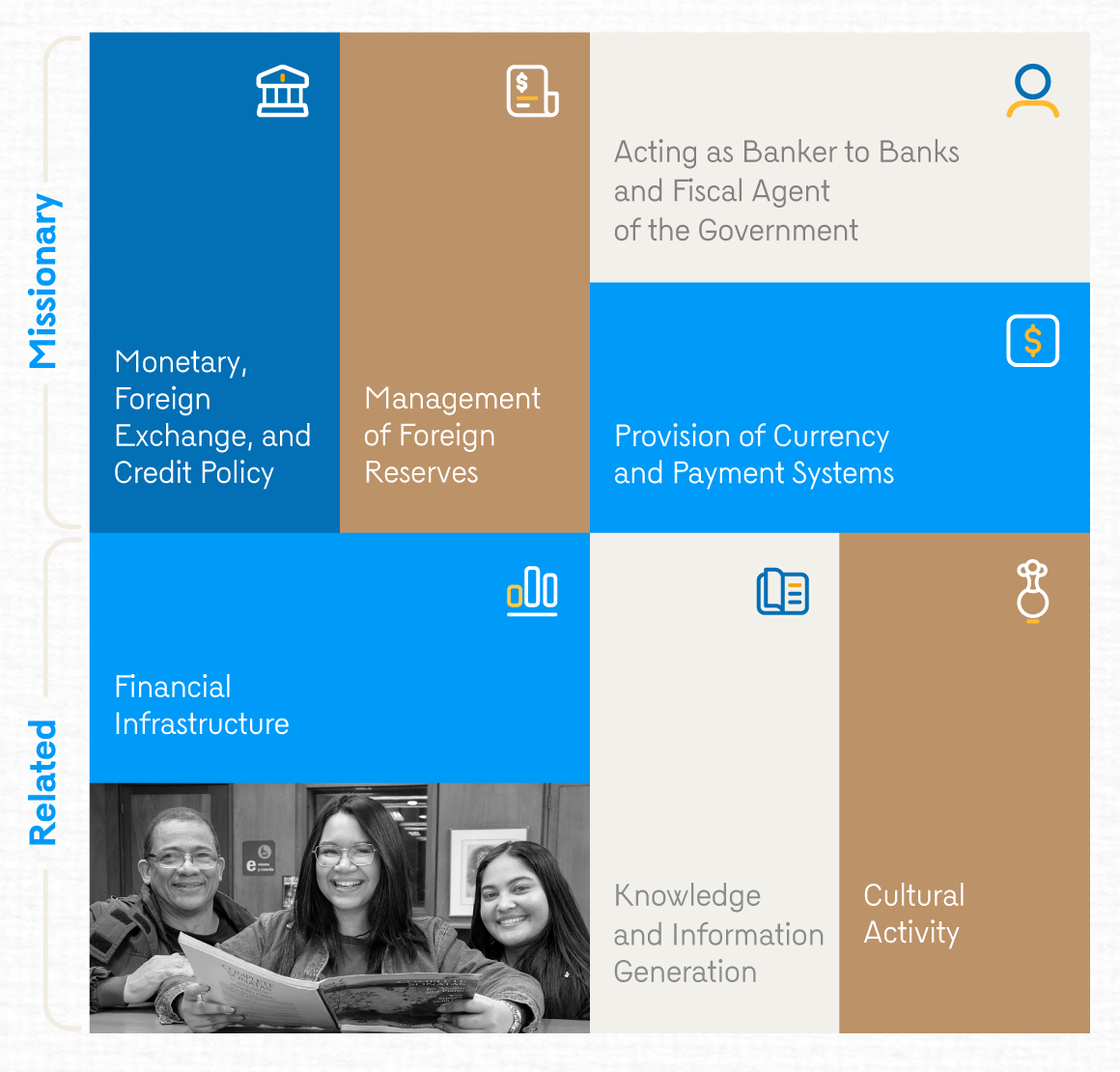
It should be noted that the Bank periodically issues reports to Congress, as well as complementary reports that include the development of its missionary and related functions.
1. Missionary Functions and Services
a. Monetary and Foreign Exchange Policy
The main objective of monetary policy is to preserve the purchasing power of currency in coordination with the general economic policy, together with the stabilization of output and employment at their sustainable long-term levels. To this end, the Bank seeks to keep inflation under control and to support macroeconomic and financial stability, thereby contributing to the creation of appropriate conditions for sustainable economic growth by:
- Defining monetary and foreign exchange policies, which include the criteria, parameters, and intervention instruments.
- Implementing monetary and foreign exchange policies, which include:
- Assessing and deciding on the need for monetary and foreign exchange intervention.
- Issuing monetary and foreign exchange regulations within the scope of its authority.
- Communicating and disseminating its policy decisions.
- Contributing to financial stability by developing the following activities:
- Monitoring the financial system and financial markets using a systemic approach.
- Contributing to the development of payment systems and financial market infrastructure.
- Regulating the large-value payment system.
- Facilitating liquidity to the payment system.
- Acting as lender of last resort to credit institutions.
b. Provision of Currency and Payment Systems
As the issuer of legal currency, the Bank is responsible for ensuring payments in the economy. In this regard, it exercises the state function of issuing legal currency on an exclusive and non-delegable basis. Consequently, it carries out the production, issuance, provision, and destruction of currency. Likewise, it manages the large-value payment system and the centralized components that enable the interoperability of retail-value instant payments, which facilitate funds transfers for the settlement of economic transactions.
The functions and services provided to fulfill these objectives are:
- Carrying out the production, issuance, provision, and destruction of currency.
- Managing the large-value payment infrastructure (Sistema de Cuentas de Depósito, CUD, in Spanish), which is the central backbone of the country’s financial infrastructure.
- Facilitating connectivity and functionality for all clearing and settlement arrangements that interact with the CUD..
- Regulating interoperability and promoting the scalability agenda of retail-value instant payment systems.
c. Acting as Banker to all Banks and as Fiscal Agent of the Government
The Bank acts as fiscal agent of the Government and provides it with services and technical assistance in matters related to the Bank’s nature and functions.
The functions and services currently provided by the Bank, among others, include:
- Participating in the definition of credit policy and defining its regulatory objectives in coordination with the National Government.
- Issuing credit regulations within the scope of its authority.
- Serving as Government’s agent for the issuance, placement, and administration of public debt securities.
- Providing the National Government and other public institutions as determined by the BDBR with the technical assistance required in matters related to the Bank’s nature and functions.
- Managing public funds as authorized by the law.
d. Management of Foreign Reserves
The Bank manages the nation’s foreign reserves under strict safety, liquidity, and profitability criteria. In exercising this function, the Bank seeks to manage foreign reserves in a manner that benefits the public interest and the economy as a whole.
2. Related Functions and Services
a. Financial Infrastructure
The Bank contributes to the sound functioning of payment systems through mechanisms that promote efficient settlement of transactions, optimization of financial resource management, and provision of intraday liquidity.
The functions and services currently provided are:
- Managing the Electronic Trading System (Sistema Electrónico de Negociación, SEN, in Spanish).
- Managing the Central Securities Depository (Depósito Central de Valores, DCV, in Spanish).
- Managing the Electronic Check Clearing (Compensación Electrónica de Cheques, CEDEC, in Spanish) and the Check Clearing House at designated branch offices.
- Managing the National Interbank Electronic Clearing House (Cámara de Compensación Electrónica Nacional Interbancaria, CENIT, in Spanish) and the Instant Retail-Value Payment System, Drixi, to facilitate the development and innovation of services associated with retail-value payments.
b. Generation of Knowledge and Information
Banco de la República contributes to the generation of knowledge through economic and financial research; the production and dissemination of statistical series in accordance with international standards; and the promotion of economic education related to central banking functions. Additionally, the Bank contributes to improving the level of education and specialized knowledge by sponsoring graduate studies.
The generation of knowledge and information is carried out through:
- Economic research.
- Generation and dissemination of statistical information.
- Organization of and participation in seminars, forums, academic events, and research networks.
- Sponsorships for graduate studies.
- Publications.
- Economic education related to central banking functions.
c. Cultural Activity
The Bank contributes to the proper management of the Nation’s cultural heritage, represented in its bibliographic, archaeological, art, numismatic, and philatelic collections, as well as in musical activities. This includes the preservation, research, and public access to these collections through its network of libraries, museums, and cultural centers with a regional presence. The Bank’s cultural work contributes to citizenship building, knowledge management, and closing gaps in access to knowledge.
III. Strategic Themes
While the SP 26-29 maintains the strategic themes defined in the Strategic Plan for 2022-2025 (except for climate change, which has been incorporated into each of the other strategic themes within this new planning cycle), the emphasis on new scopes and targets is defined through the new objectives presented below.
Accordingly, as mentioned, the Bank seeks to consolidate the progress achieved in previous years and to guide and prioritize its actions in light of the trends that will impact central banking. Additionally, the Bank will seek to expand its scope in sustainability-related matters, thereby further consolidating the progress achieved regarding climate change. Graph 2 presents the eight strategic themes:
Graph 2. Strategic Themes
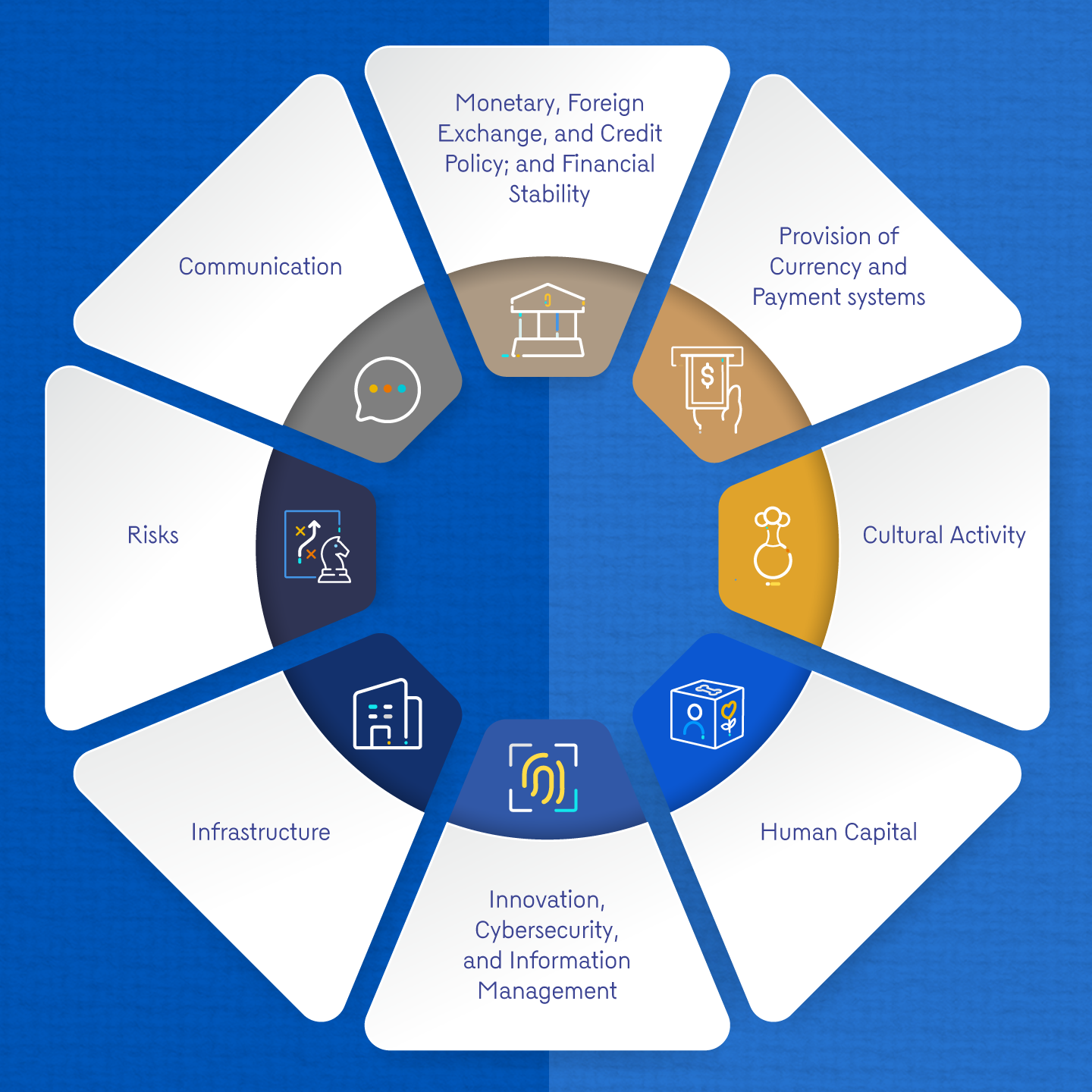
The objectives for each of the strategic themes are presented below.
A. Monetary, Foreign Exchange, and Credit Policy; and Financial Stability
- To continue strengthening the analysis of monetary policy and adapt it to the changing economic conditions.
- To adapt information capture, processing, and dissemination systems to technological developments, financial innovations, changes in information sources, and updates to international standards.
- To promote and lead the development of regulation and monitoring of the digital asset market within the scope of the Bank’s competencies.
- To improve the efficiency and accessibility of Temporary Liquidity Support framework (ATL, in Spanish).
- To strengthen the existing regulatory framework for non-bank financial institutions, with an emphasis on Collective Investment Funds (CIFs).
- To expand the active foreign reserves management framework, including the possibility of considering specialized mandates.
- To improve efficiency and security in financial portfolio management by modernizing the Bank’s technological infrastructure.
- To deepen the foreign exchange market, particularly the derivatives segment, through the assessment and implementation of initiatives to improve access and liquidity.
- To maintain the productivity and thematic range of the Bank’s research and its network of researchers (Red de Investigadores, in Spanish) to contribute to the knowledge of the Colombian economy.
- To improve the timeliness, security, and efficiency of the research process by integrating disaggregated data sources to be used by the Bank’s researchers.
B. Provision of Currency and Payment systems
- To strengthen security, prevent counterfeiting, and increase the durability of banknotes by adopting new and environmentally sustainable technologies.
- To assess alternatives to update the coin family under a cost-efficient and environmentally sustainable scheme.
- To reduce the carbon footprint generated by the Bank by optimizing the energy efficiency of industrial plants by improving the performance of equipment used in production and support processes.
- To improve efficiency in the cash cycle by deepening third-party participation to enhance the quality and availability of banknotes and coins, particularly in remote areas of the country, and to optimize inventory activities by using new information sources and advanced data-processing technologies.
- To complete the modernization of the Treasury’s technological systems that support cash management and the valuables movement system.
- To develop the instant electronic payments ecosystem by regulating and implementing new use cases and transactional services within Bre-B.
- To strengthen the supply of efficient and secure cross-border payment options, considering interoperability between large-value and retail-value payment systems and experimenting with wholesale Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
- To promote innovation in the financial market infrastructures managed by the Bank, particularly by leading the industry-wide adoption of ISO 20022 messaging standard and functionalities such as automated (algorithmic) trading, and by advancing experimentation in digital assets.
- To complete the modernization of the Electronic Trading System (Sistema Electrónico de Negociación, SEN, in Spanish).
C. Cultural Activity
- To ensure the distinctiveness, relevance, and sustainability of the Bank’s cultural management by incorporating new cultural management models.
- To strengthen research capacity on the materiality of heritage collections, so as to contribute to their preservation and sustainability and enhance their relevance for present and future generations.
- To promote research on Colombian historical heritage, knowledge management, access to information, and co-creation with specific audiences within the Library Network.
- To foster the appropriation of natural heritage and the generation of environmental awareness with regional relevance through cultural management projects based on heritage collections.
D. Human Capital
- To transform the Bank’s employee experience by strengthening professional development, positive work environment, and a strong employer brand to attract, engage, and retain human talent.
- To promote the strengthening of diversity, equity, and inclusion policies within the Bank as key pillars to consolidate a more representative culture aligned with institutional values.
E. Infrastructure
- To consolidate the Bank’s current infrastructure modernization plan by ensuring comprehensive project management per the timelines established.
- To complete the assessment of the Bank’s buildings in terms of seismic vulnerability and, based on results and on the needs identified for corporate, industrial, treasury, and cultural activities, to prioritize projects for the subsequent phases of the infrastructure modernization plan.
- To systematically incorporate best design and construction practices into the Bank’s infrastructure projects, integrating updates related to climate change, sustainability, energy efficiency, renewable energy, carbon footprint reduction, and diversity.
F. Risks
- To consolidate the role of the Risk Management Office in carrying out risk management independently from business areas in the Bank’s new projects, processes, and services.
- To define and implement the Bank’s strategic risk and opportunity management model, with an emphasis on areas such as emerging risks.
- To strengthen the Business Continuity Management System in line with best practices in this field.
- To consolidate the anti-bribery and anti-corruption compliance function under the responsibility of the Bank’s second line of defense.
- To coordinate the implementation of climate change and sustainability policies defined across the different areas of the Bank related to risk management regulations.
G. Innovation, Cybersecurity, and Information Management
- To promote innovation and digital transformation by using emerging technologies and fostering a culture of user ownership and autonomy in technological matters.
- To increase cybersecurity maturity levels and promote the adoption of resilience-oriented models, proactively anticipating and responding to a dynamic and growing threat environment, in line with the objectives of continuity, trust, and operational sustainability.
- To enhance the strategic use of data to optimize operations and decision-making by strengthening current technologies and methodologies under principles of information security and preservation.
- To strengthen and evolve the technological environment to achieve the capacity and availability levels required by global dynamics while maintaining balance between efficiency, cost, and autonomy in the provision of information technology (IT) infrastructure.
H. Communication
- To define a new external communication strategy for Banco de la República.
IV. Monitoring of the Strategic Plan
To monitor the Strategic Plan, the Administrative Council approves indicators, baselines, and targets for the objectives included in each of the strategic themes. Progress under the Plan and the results of these indicators are presented semi-annually to the Administrative Council. The Board of Directors reviews the Strategic Plan annually.
1 ↑ Political Constitution of Colombia of 1991, TITLE XII (ECONOMIC REGIME AND PUBLIC FINANCE), CHAPTER 6: CENTRAL BANKING.
2 ↑ The strategic objectives related to climate change, which in the Strategic Plan 2022–2025 were presented as a standalone theme, were integrated into the other strategic themes defined for the SP 26–29. With this integration, actions aimed at achieving these objectives are addressed within the theme that directly develops them.































































