Foreign Reserves
Colombia's foreign reserves are administered by Banco de la República (the Central Bank of Colombia). This function must be performed in the public interest, for the benefit of the national economy, and to facilitate the country's international payments. The investment of reserve assets is subject to the criteria of security, liquidity, and return.
What are foreign reserves?
Foreign reserves are external assets under the control of monetary authorities such as Banco de la República (the Central Bank of Colombia), expressed mainly in foreign currency. For an external asset to be part of the foreign reserves, it must be under the direct and effective control of the monetary authority and must be immediately available for use.
What are foreign reserves for?
Foreign reserves are used to protect the country from external shocks that may affect both trade and financial flows and, depending on their magnitude, may threaten macroeconomic and financial stability. Reserves have two main functions: facilitating access to the international capital market and implementing the Bank's foreign exchange intervention.
In the first case, having an adequate level of foreign reserves indicates that the country has sufficient capacity to cover its foreign currency obligations in times of crisis or high market stress. Therefore, foreign reserves facilitate the country's access to international markets since they serve as a guarantee to international markets. In the second case, Banco de la República (the Central Bank of Colombia) may use foreign reserves to correct failures in the functioning of the foreign exchange market or to address excessive exchange rate misalignments that could negatively affect compliance with the inflation target or threaten financial stability.
How are foreign reserves invested?
Reserves are managed based on the investment guidelines established by the Foreign Reserves Committee (CRI in Spanish), which comprises the same members of the Board of Directors of Banco de la República (the Central Bank of Colombia). These guidelines include a set of investment rules or criteria to guarantee that the reserves are invested with security, liquidity, and return as priorities, seeking portfolio diversification and adequate risk management. Reserves are mainly invested in debt instruments of governments, government-related entities (quasi-government), and bank and corporate debt.
Banco de la República (the Central Bank of Colombia), as the institution that is primarily responsible for managing the reserves, continuously monitors the investment portfolios to ensure compliance with these investment guidelines.
To ensure compliance with the security, liquidity, and profitability criteria, foreign reserves are invested in assets with the highest credit risk ratings, in highly liquid instruments, and where the highest level of return is sought while minimizing risk.
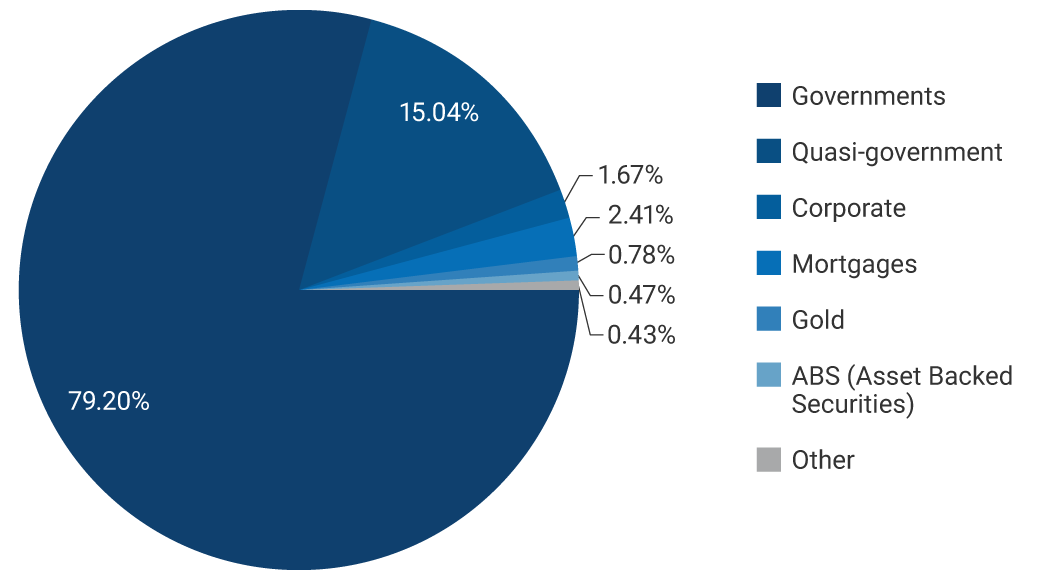
Graph 1. Composition of the investment portfolio by sector (information as of 31 March 2025)
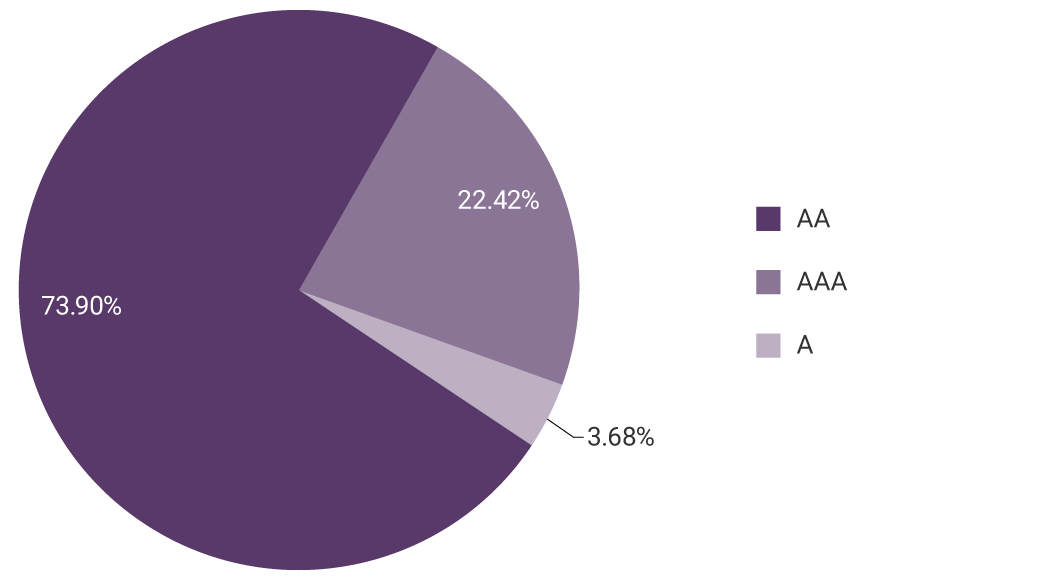
Graph 2. Distribution of investments by credit rating (information as of 31 March 2025)
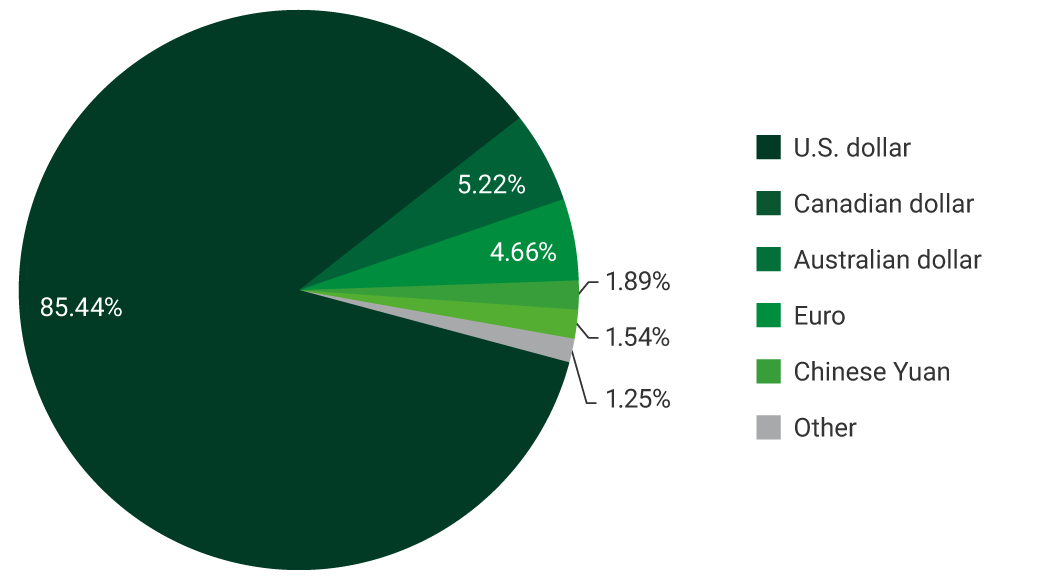
Graph 3. Foreign exchange composition of the investment portfolio (information as of 31 March 2025)
Graph 4. Composition of the investment portfolio by maturity (information as of 31 March 2025)
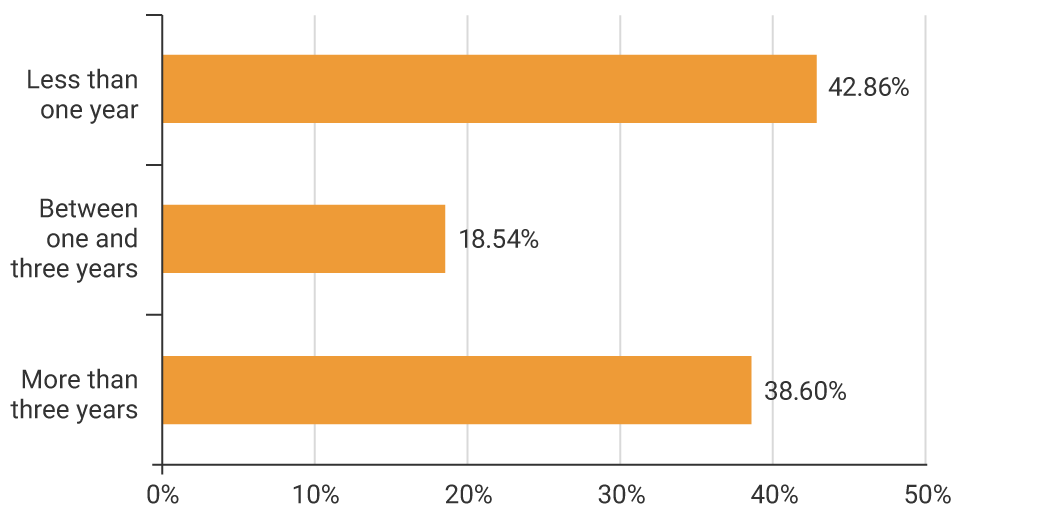
Who manages foreign reserves?
Foreign reserve investment is carried out on two fronts: internally, managed by Banco de la República (the Central Bank of Colombia), and externally through a program of external investment management firms. In the first case, the Sub-Directorate for Portfolio Management of Banco de la República (the Central Bank of Colombia) is in charge of investing approximately 72% of the total reserves. In turn, the external management program represents approximately 28% of the resources.
External investment management firms are institutions specialized in managing investment portfolios. Many central banks use them to manage their foreign reserves. On the one hand, hiring external managers seeks to add value to the reserve portfolio through broader investment diversification. On the other hand, it enhances the professionalism with which portfolios are managed, provides access to the analysis of international markets by these firms, and contributes to the training of central bank staff involved in reserve management. The selected firms have extensive experience and knowledge of the financial markets as well as sophisticated infrastructures.































































