Economic-knowledge: Monetary Policy
Monetary policy is a key component of a country’s macroeconomic policy. It includes a set of actions through which the central Bank seeks to achieve specific objectives, such as a low and stable inflation that preserves the purchasing power of money and contributes to maintaining sustainable economic growth in a context of financial stability.
For monetary policy to be effective, it is necessary to have certain basic principles to ensure credibility and the ability to act. These are: 1) to establish clear and well-defined objectives; 2) to have operational independence so that actions are consistent with the results of its analysis and projections, without external interferences; 3) to adopt a clear operational scheme and a mechanism of accountability, so that society is aware of the Central Bank’s actions; 4) to have a mid-term policy prospect consistent with the capacity of its instruments to influence economic variables, and 5) to have transparent communication policies.
The effective monetary policy schemes in most countries are based on a solid (constitutional) institutional structure that provides independence and establishes long-term objectives, such as achieving price stability. In order to achieve this, the monetary authority sets an intermediate target consisting of choosing a single variable that can be observed and measured (for example, exchange rate, money growth, inflation forecast close to a target, among others) to use it as a guide, given that none of these variables is entirely controlled by the monetary authority.
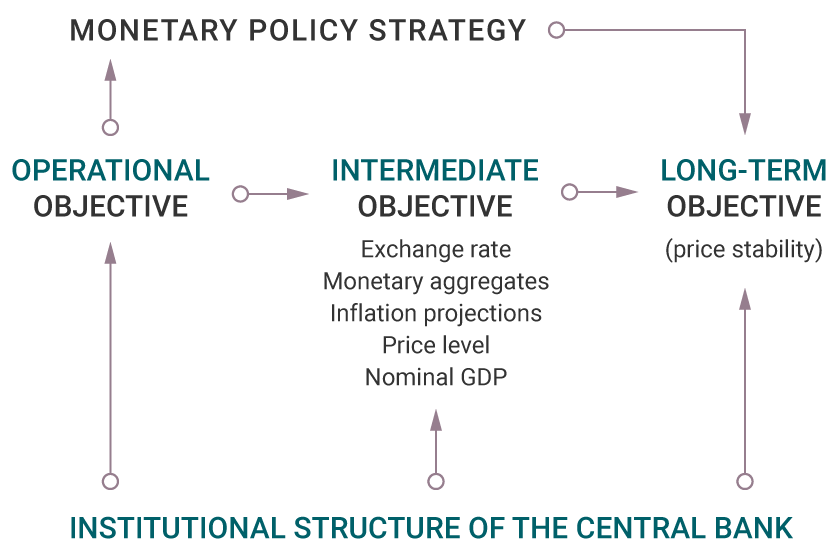
What the monetary authority can control is an instrument, which consists of a short-term variable that it can freely choose, such as the interest rate of repo operations with commercial banks (known as operational objective), which should be directly linked to the intermediate objective. A repo is a sales operation of an asset, such as financial instruments, in exchange for an amount of money with the agreement to repurchase it.
| Elements of the inflation targeting scheme | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Operational objective | Short-term interest rate | ||
| Middle-term objective | Inflation forecast | ||
| Long-term objective | Price stability | = | Target inflation |
In this way, the monetary authority modifies the short-term variable to achieve the intermediate objective, which should lead to meeting the established long-term objective.
A credible monetary policy provides a favorable economic context, by introducing a countercyclical handling mechanism, which contributes to dampening the effects of internal or external shocks that may affect the economy and may compromise the population's well-being.
Inflation targeting
In order to comply with the constitutional mandate of maintaining the purchasing power of currency and promoting a sustainable economic growth, since the end of the 1990s, the Board of Directors of Banco de la República (the Central Bank of Colombia) adopted a monetary policy scheme called inflation targeting. This is oriented towards meeting an inflation target that allows to maintain inflation expectations around that target (for the Colombian case it is 3.0%), as well as striving to achieve the maximum sustainable level of production and employment. This strategy is based on explicitly communicating to the public that all Bank’s decisions will be focused on keeping inflation low and stable, and thus anchoring the inflation expectations in the central target announced by the Board of Directors. When the monetary authority has credibility and the expectations of low inflation are consolidated, it is highly probable that they will affect the economic agents’ and population’s behavior and, therefore, the growth rate of prices that would be close to the target established by Banco de la República.
Characteristics
Following the most important characteristics of this monetary policy strategy, the Board of Directors must:
 | Announce a quantitative inflation target/1. |
 | Have the public recognize that the explicit and main objective of the monetary policy is to keep inflation low and stable. |
 | Have a monetary policy instrument that influences the short-term, middle-term, and long-term objectives. |
 | Give more importance to the inflation forecast in the execution of the monetary policy. |
 | Adopt a flexible exchange rate that ensures monetary policy autonomy. |
 | Have a high level of transparency in its communications and accountability to society. |
| 1/ n Colombia’s measurement, inflation refers to the annual variation of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) calculated by the National Administrative Department of Statistics (DANE, in Spanish). | |































































